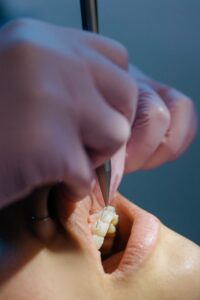
Introduction
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is an inflammatory condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It starts as gingivitis and, if unaddressed, can lead to tooth loss due to the destruction of the tissues holding the teeth in place. According to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly half of the American adults some form of periodontal disease, making it one of the most common dental issues in the U.S. The condition poses a significant impact on oral health and quality of life by causing pain, discomfort, and difficulty in chewing, and not to mention, it adversely affects one’s appearance and self-esteem. The early detection and prevention of periodontal disease plays a vital role in preserving oral health. When caught in its early stages, periodontal disease is easier to treat and manage, reducing the risk of severe complications.
Comprehending Periodontal Disease
A healthy mouth teems with microbial life. However, changes in diet, hygiene, stress, or immune health can disrupt this balance, allowing harmful bacteria to proliferate, leading to gum infections such as periodontal disease. Periodontal disease results from the overgrowth of certain bacteria in the mouth, mainly due to poor oral hygiene. The body’s reaction to these bacteria causes inflammation and, over time, this chronic inflammation can erode the tooth’s supporting structures. Periodontal disease progresses in stages, starting with minor gum inflammation (gingivitis) and gradually progressing to more severe conditions, including periodontitis and advanced periodontitis, which is characterized by severe gum recession, bone loss, and eventual tooth loss.
Early Signs of Periodontal Disease
Early symptoms include red, swollen gums that bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing. Additionally, other signs can involve chronic bad breath, mouth sores, or a change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite. During a dental examination, the dentist will look for signs of inflammation, gum recession, plaque, and tartar build-up. Furthermore, they may also conduct a periodontal probing to determine if there has been a loss of bone around the teeth. Certain factors, such as smoking, genetic predisposition, poor diet, and underlying conditions like diabetes, can significantly enhance the progression of periodontal disease.
Prevention Strategies for Periodontal Disease
Regular brushing and flossing are fundamental to maintaining oral hygiene. It’s recommended to brush twice a day and floss at least once a day to remove plaque and prevent build-up. Regular dental check-ups are crucial to detect signs of periodontal disease early. Professional cleanings can remove plaque and tartar, which cannot be removed by brushing and flossing alone. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can promote gum health. Lifestyle choices such as quitting smoking and reducing stress also contribute to preventing periodontal disease.
Role of Professional Dental Care in Managing Periodontal Disease
Early intervention by a dentist can halt the progress of periodontal disease and provide treatment options. Disease management may involve professional cleanings, antibiotics, or more advanced treatments depending on the severity of the condition. Advanced periodontal disease may require treatments such as scaling and root planing, tissue or bone grafts, or periodontal surgery. After treatment, maintaining good oral hygiene, following a healthy diet, and abstaining from detrimental habits such as smoking is crucial for preventing recurrence.
Summary and Key Takeaways
Periodontal disease is a common yet preventable dental issue. Early symptoms like bleeding or swollen gums should not be overlooked. Regular brushing, flossing, and dentist visits, along with a healthy diet and lifestyle, can go a long way in maintaining gum health.
FAQs
- Q: What are the early signs of periodontal disease? A: Early signs include red or swollen gums, bleeding during brushing, bad breath, and gum sensitivity. Consult a dentist if these symptoms arise for timely intervention.
- Q: How can I prevent periodontal disease? A: Preventive measures involve regular brushing, flossing, using mouthwash, attending dental check-ups, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco. Healthy lifestyle choices contribute significantly to prevention.
- Q: Is gum disease hereditary? A: While genetics play a role, periodontal disease is not directly inherited. If there’s a family history, maintaining strict oral hygiene and regular check-ups helps minimize the risk.
- Q: Can hormonal changes affect the risk? A: Yes, hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can increase susceptibility. Those experiencing such changes should prioritize diligent oral care.
- Q: Are certain groups more at risk? A: Yes, smokers, diabetics, individuals with a weakened immune system, and those with a family history are more vulnerable. Pregnant and menopausal individuals should also be attentive to oral health. Regular professional dental care is crucial for these at-risk groups.
Our Reading dental clinic is committed to providing you with a beautiful smile every time you visit us. Whether you need Periodontal (Gum) Treatment or any other dental services, our team of highly trained dentists is here to provide you with the highest quality care. Our aim at Smiles in Reading is to give you a smile that is both comfortable and respectful. With online appointment scheduling, you can now receive dental care of the highest quality. Our dental professionals are here to help you enhance your smile and teeth.